Page 215 - CITS - ED - Mechanical
P. 215
ENGINEERING DRAWING - CITS
Term Abbreviations/Symbol Term Abbreviations/Symbol
Pressure p Square SQ,
Pattern number PATT NO. Standard STD
Quantity QTY Square centimetre Cm 2
Radius R Square metre m 2
Reference REF Square millimetre mm 2
Required REQD Symmetrical SYM
Revolution per minute rpm Standard wire gauge SWG
Rockwell hardness `A' scale HRA Tee (Structural section) T
Rockwell hardness `B' scale HRB Threads per inch TPI
Rockwell hardness `C' scale HRC Temperature TEMP
Right hand RH Time t
Round head RD.HD Tanne t
Second of angle " Undercut U' CUT
Volt V
Serial number SL.No.
Volume VOL
Second of time S
Vickers hardness HV
Spot face SF
Weight W
Screwed SCR
Surface quality
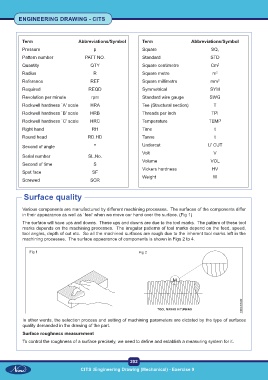
Various components are manufactured by different machining processes. The surfaces of the components differ
in their appearance as well as `feel' when we move our hand over the surface. (Fig 1)
The surface will have ups and downs. These ups and downs are due to the tool marks. The pattern of these tool
marks depends on the machining processes. The irregular patterns of tool marks depend on the feed, speed,
tool angles, depth of cut etc. So all the machined surfaces are rough due to the inherent tool marks left in the
machining processes. The surface appearance of components is shown in Figs 2 to 4.
Fig 1 Fig 2
In other words, the selection process and setting of machining parameters are dictated by the type of surfaces
quality demanded in the drawing of the part.
Surface roughness measurement
To control the roughness of a surface precisely, we need to define and establish a measuring system for it.
202
CITS :Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 9