Page 200 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 200
WELDER - CITS
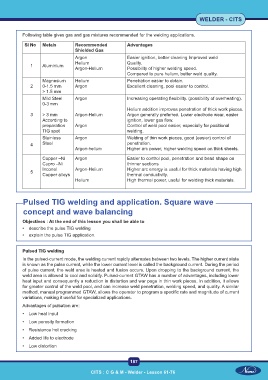
Following table gives gas and gas mixtures recommended for the welding applications.
Sl No Metals Recommended Advantages
Shielded Gas
Argon Easier ignition, better cleaning Improved weld
Helium Quality.
1 Aluminium
Argon-Helium Possibility of higher welding speed.
Compared to pure helium, better weld quality.
Magnesium Helium Penetration easier to obtain.
2 0-1.5 mm Argon Excellent cleaning, pool easier to control.
> 1.5 mm
Mild Steel Argon Increasing operating flexibility. (possibility of overheating).
0-3 mm
Helium addition improves penetration of thick work pieces.
3 > 3 mm Argon-Helium Argon generally preferred. Lower electrode wear, easier
According to ignition, lower gas flow.
preparation Argon Control of weld pool easier, especially for positional
TIG spot welding.
Stainless Argon Welding of thin work pieces, good (easier) control of
4 Steel penetration.
Argon-helium Higher arc power, higher welding speed on thick sheets.
Copper –Ni Argon Easier to control pool, penetration and bead shape on
Cupro –Ni thinner sections
Inconel Argon-Helium Higher arc energy is useful for thick materials having high
5
Copper alloys thermal conductivity.
Helium High thermal power, useful for welding thick materials.
Pulsed TIG welding and application. Square wave
concept and wave balancing
Objectives : At the end of this lesson you shall be able to
• describe the pulse TIG welding
• explain the pulse TIG application.
Pulsed TIG welding
In the pulsed-current mode, the welding current rapidly alternates between two levels. The higher current state
is known as the pulse current, while the lower current level is called the background current. During the period
of pulse current, the weld area is heated and fusion occurs. Upon dropping to the background current, the
weld area is allowed to cool and solidify. Pulsed-current GTAW has a number of advantages, including lower
heat input and consequently a reduction in distortion and war page in thin work pieces. In addition, it allows
for greater control of the weld pool, and can increase weld penetration, welding speed, and quality. A similar
method, manual programmed GTAW, allows the operator to program a specific rate and magnitude of current
variations, making it useful for specialized applications.
Advantages of pulsation are:
• Low heat input
• Low porosity formation
• Resistance hot cracking
• Added life to electrode
• Low distortion
187
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 61-76