Page 204 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 204
WELDER - CITS
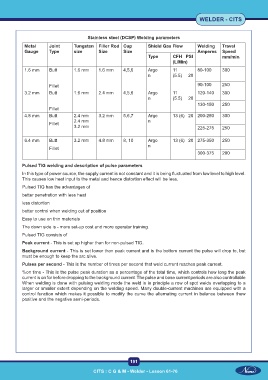
Stainless steel (DCSP) Welding parameters
Metal Joint Tungsten Filler Rod Cup Shield Gas Flow Welding Travel
Gauge Type size Size Size Amperes Speed
Type CFH PSI mm/min
(L/Min)
1.6 mm Butt 1.6 mm 1.6 mm 4,5,6 Argo 11 80-100 300
n (5.5) 20
Fillet 90-100 250
3.2 mm Butt 1.6 mm 2.4 mm 4,5,6 Argo 11 120-140 300
n (5.5) 20
130-150 250
Fillet
4.8 mm Butt 2.4 mm 3.2 mm 5,6,7 Argo 13 (6) 20 200-250 300
2.4 mm n
Fillet
3.2 mm 225-275 250
6.4 mm Butt 3.2 mm 4.8 mm 8, 10 Argo 13 (6) 20 275-350 250
n
Fillet
300-375 200
Pulsed TIG welding and description of pulse parameters
In this type of power source, the supply current is not constant and it is being fluctuated from low level to high level.
This causes low heat input to the metal and hence distortion effect will be less.
Pulsed TIG has the advantages of
better penetration with less heat
less distortion
better control when welding out of position
Easy to use on thin materials
The down side is - more set-up cost and more operator training.
Pulsed TIG consists of
Peak current - This is set up higher than for non-pulsed TIG.
Background current - This is set lower than peak current and is the bottom current the pulse will drop to, but
must be enough to keep the arc alive.
Pulses per second - This is the number of times per second that weld current reaches peak current.
%on time - This is the pulse peak duration as a percentage of the total time, which controls how long the peak
current is on for before dropping to the background current. The pulse and base current periods are also controllable
When welding is done with pulsing welding mode the weld is in principle a row of spot welds overlapping to a
larger or smaller extent depending on the welding speed. Many double-current machines are equipped with a
control function which makes it possible to modify the curve the alternating current in balance between thew
positive and the negative semi-periods.
191
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 61-76