Page 78 - CITS - ED - Mechanical
P. 78
ENGINEERING DRAWING - CITS
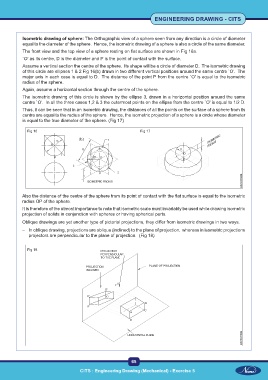
Isometric drawing of sphere: The Orthographic view of a sphere seen from any direction is a circle of diameter
equal to the diameter of the sphere. Hence, the isometric drawing of a sphere is also a circle of the same diameter.
The front view and the top view of a sphere resting on flat surface are shown in Fig 16a.
`O' as its centre, D is the diameter and P is the point of contact with the surface.
Assume a vertical section the centre of the sphere. Its shape will be a circle of diameter D. The isometric drawing
of this circle are ellipses 1 & 2 Fig 16(b) drawn in two different vertical positions around the same centre `O'. The
major axis in each case is equal to D. The distance of the point P from the centre `O' is equal to the isometric
radius of the sphere.
Again, assume a horizontal section through the centre of the sphere.
The isometric drawing of this circle is shown by the ellipse 3, drawn in a horizontal position around the same
centre `O'. In all the three cases 1,2 & 3 the outermost points on the ellipse from the centre `O' is equal to 1/2 D.
Thus, it can be seen that in an isometric drawing, the distances of all the points on the surface of a sphere from its
centre are equal to the radius of the sphere. Hence, the isometric projection of a sphere is a circle whose diameter
is equal to the true diameter of the sphere. (Fig 17)
Fig 16 Fig 17
Also the distance of the centre of the sphere from its point of contact with the flat surface is equal to the isometric
radius OP of the sphere.
It is therefore of the utmost importance to note that isometric scale must invariably be used while drawing isometric
projection of solids in conjunction with spheres or having spherical parts.
Oblique drawings are yet another type of pictorial projections, they differ from isometric drawings in two ways.
– In oblique drawing, projections are oblique (inclined) to the plane of projection. whereas in isometric projections
projectors are perpendicular to the plane of projection. (Fig 18)
Fig 18
65
CITS : Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 5