Page 236 - CITS - ED - Mechanical
P. 236
ENGINEERING DRAWING - CITS
Geometrical tolerance
Definition of geometrical tolerance
Geometrical tolerance is the maximum permissible overall variation of form or position of a feature.
Reason for using geometrical tolerance
This will help the operator to produce the components, particularly those parts which must fit together precisely.
The idea is to have an international system which will overcome the usual language barrier. This is achieved by
the use of symbols which represent geometrical characteristics.
Form: Straightness, flatness, roundness, cylindricity and profile of a line and a surface.
Attitude: Parallelism, squareness and angularity.
Location: Position, concentricity and symmetry.
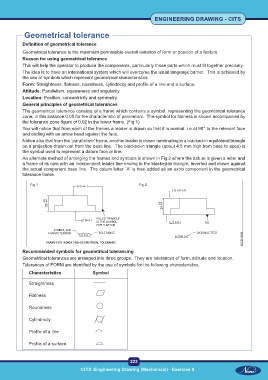
General principles of geometrical tolerances
The geometrical tolerance consists of a frame which contains a symbol, representing the geometrical tolerance
zone; in this instance 0.05 for the characteristic of parallelism. The symbol for flatness is shown accompanied by
the tolerance zone figure of 0.02 in the lower frame. (Fig 1)
You will notice that from each of the frames a leader is drawn so that it is normal, i.e at 90° to the relevant face
and ending with an arrow head against the face.
Notice also that from the `parallelism' frame, another leader is drawn terminating in a blacked-in equilateral triangle
on a projection drawn out from the base line. The blacked-in triangle (about 4.5 mm high from base to apex) is
the symbol used to represent a datum face or line.
An alternate method of arranging the frames and symbols is shown in Fig 2 where the datum is given a letter and
a frame of its own with an independent leader line ending in the blacked-in triangle, inverted and drawn against
the actual component base line. The datum letter `A' is then added as an extra component in the geometrical
tolerance frame.
Fig 1 Fig 2
Recommended symbols for geometrical tolerancing
Geometrical tolerances are arranged into three groups. They are tolerances of form, attitude and location.
Tolerances of FORM are identified by the use of symbols for the following characteristics.
Characteristics Symbol
Straightness
Flatness
Roundness
Cylindricity
Profile of a line
Profile of a surface
223
CITS :Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 9 CITS :Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 9