Page 72 - CITS - ED - Mechanical
P. 72
ENGINEERING DRAWING - CITS
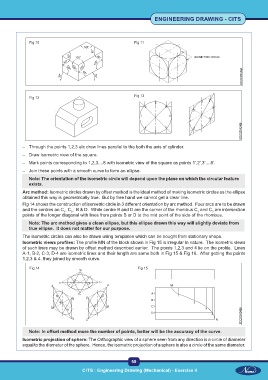
Fig 10 Fig 11
Fig 12 Fig 13
– Through the points 1,2,3 etc draw lines parallel to the both the axis of cylinder.
– Draw isometric view of the square.
– Mark points corresponding to 1,2,3....8 with isometric view of the square as points 1’,2’,3’....8’.
– Join these points with a smooth curve to form an ellipse.
Note: The orientation of the isometric circle will depend upon the plane on which the circular feature
exists.
Arc method: Isometric circles drawn by offset method is the ideal method of making isometric circles as the ellipse
obtained this way is geometrically true. But by free hand we cannot get a clear line.
Fig 14 shows the construction of isometric circle in 3 different orientation by arc method. Four arcs are to be drawn
and the centres an C , C , B & D. While centre B and D are the corner of the rhombus C and C are intersection
1
2
2
1
points of the longer diagonal with lines from points B or D to the mid point of the side of the rhombus.
Note: The arc method gives a clean ellipse, but this ellipse drawn this way will slightly deviate from
true ellipse. It does not matter for our purpose.
The isometric circles can also be drawn using templates which can be bought from stationary shops.
Isometric views profiles: The profile MN of the block shown in Fig 15 is irregular in nature. The isometric views
of such lines may be drawn by offset method described earlier. The points 1,2,3 and 4 lie on the profile. Lines
A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4 are isometric lines and their length are same both in Fig 15 & Fig 16. After getting the points
1,2,3 & 4, they joined by smooth curve.
Fig 14 Fig 15
Note: In offset method more the number of points, better will be the accuracy of the curve.
Isometric projection of sphere: The Orthographic view of a sphere seen from any direction is a circle of diameter
equal to the diameter of the sphere. Hence, the isometric projection of a sphere is also a circle of the same diameter.
59
CITS : Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 4 CITS : Engineering Drawing (Mechanical) - Exercise 4